Thailand -- School-age
Thailand
Official Name: Kingdom of Thailand (former Siam)
Government Type: Constitutional Monarchy and a Parliamentary Democracy
Capital: Bangkok
County's inhabitants: Thai (singular and plural)
Abbreviation: TH
Currency: Baht (S$, THB)
Official Languages: Thai
Population: Thai 97.5%, Burmese 1.3%, other 1.1%, unspecified <.1% (2015 est.)
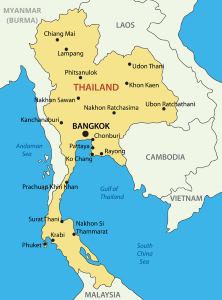
The country of Thailand is located in Southeastern Asia. It lays south of the mainland part of Malaysia.
Thailand borders the Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand,
There ere are approximately 1,430 islands off the coast of Thailand, both in the Andaman Sea and in the Gulf of Thailand.
Thailand controls the only land route from Asia to Malaysia and Singapore.
It is said that Thailand is shaped like an elephants head with a very long, skinny trunk.
History
Ban Chiang is an archaeological site in Thailand. Pottery, jewelry, and tools have been dug up in this area that date from 200 BC to 300 AD.

Ceramic bowl from
Ban Chiang site.
Thailand was known as Siam until changing its name in 1939. The word "Thai" means free. Threfore Thailand means "Land of the Free".
Siamosaurus (meaning "Siamese lizard") is a dinosaur that lived in what is now known as China and Thailand. Most of the dinosaur fossils were found in northeastern Thailand.

Siamosaurus suteethorni sculpture Phu Wiang Dinosaur Museum
History of Thailand Video
Government
Thailand is a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy with the monarch as the head of state. The constitution limits the powers of the king.
Thailand has three branches of government, executive, legislative, and judicial. The ececutive branch consist of the king and the prime minister. The Prime Minister acts as the leader of the government. The prime minister is selected by elecion in the lower house of parliament and approved by the king.
The Parliament of Thailand is bicameral and is composed of the House of Representatives and the Senate. Legislation orignates from the House of Representatives. The Senate has little legislative power. It has powers on appointments to the judiciary and other government agencies.
The Judicial Branch is made up of judges selected by the monarch.
Flag of Thailand

Today's Thailand flag was changed in 1917. Thailand was one of the few Asian countries to that was never under European colonial rule. Thailand close relations with the West resulted in it becoming one of the Allies in World War I. King Rama VI changed the country's flag to honor the relationship and to give the flag a modern design.
The red is a symbol the blood shed by the Thai people for their country. White stands for religious laws and the purity of Buddhism. Blue is the color of the Monarchy that guides the country.
National Symbols

National Flower: Rachaphruek
How to pronounce ratchaphruek

National Animal: Thai Elephant

National Architecture: The Sala Thai (Thai Pavilion)
Climate
Thailand has a tropical monsoon climate that is warm, wet or hot, and humid. In southern Thailand there are two seasons, dry and wet. From June to October is the rainy season, it pours rain almost every day The southwest monsoon are usually from mid-May to September.
Land
In the north, Thailand has mountains that reach heights of more than 8,000 feet (2,400 meters). The highest point is Doi Inthanon in the Thanon Thong Chai Range at 8,415 feet (2,565 meters). The high mountains are the source of many rivers in Thailand. The rivers generally flow south to join the Chao Phraya River, the country's major river.
The northeast of Thailand consist of the Khorat Plateau an area of low hills and small lakes. It is bordered on the north and east by the Mekong River. The Mekong River forms most of the border between Thailand and Laos.
The southern region of Thailand lies on a long, thin strip of land called the Malay Peninsula. It is hilly and forested.

View west from the Doi Inthanon mountain.
Plants
Layers Of A Rainforest There are four layers of a tropical rainforest.
Tropical Rainforest plant adaptations that enables plants to live in hot, humid, and wet conditions.
Bamboo is found in Asian rainforests. It is one of the fastest growing plants and can grow over 100 feet tall.
The lotus flower is native to Southeast Asia. They are a common flower and a favorite flower in Thailand. The lotus flower is an aquatic plant that floats on water and is rooted in mud.
Animals
Thailand has a great diversity of animal life.
The Thai Elephant in Thailand is protected, so the number of wild elephants is increasing. There are only two species of elephants in the world: the African elephant and the Asian elephant. There are four subspecies of the Asian elephant: Bornean, Indian, Sri Lankan, and Sumatran. The elephants in Thailand are classed as Indian elephants. There are slight differences, the Thai elephant is smaller, has shorter front legs, and a thicker body than their Indian counterparts. (
Thailand has two native species of bear; the Asiatic Black Bear and the Malayan Sun Bear. The Black is found all over the country while the Sun Bear is found in the southern region of Thailand.
Gibbons are small apes that live in the upper canopy of the lowland rainforest of Southeast Asia.
The Common Tree Shrew area where it lives begins in Thailand, goes through the Malayan Peninsula and into Indonesia.
Slow Loris is the world's only venomous primate.
The pitta bird was rediscovered in the Khao Noi Chuchi (last lowland rainforest in Thailand) after being considered extinct.
The Red-Whiskered Bulbul in the south of Thailand the bulbul is caged for competition. The Red-Whiskered Bulbul was once commonly found throughout the country, over the past 10 years its sound has slowly disappeared from the southern forests of Thailand.
Elephant Species Differences
Thailand Is Famous For
Elephants is part of the history and national identity in Thailand. Elephants in Thailand were used in war, labor, and a form of transport. How the elephant in Thailand became a national symbol - The History of Elephants in Thailand
Thailand is known for its ruby mines. Rubies were mined near the Cambodian border. Thailand has few deposits left, it remains the main center of the world's ruby industry for cutting, treatment, and marketing of the precious ruby.
The History of Rubies in Thailand
Thailand Products
Thailand is the world's leading exporter of rice.
Wet rice: Grown in irrigated fields throughout the central plain
and in the South. Common method of growing rice in Asia by flooding fields with water. Later, when the crops mature, the fields are drained. Wet-rice cultivation (this link shows a site about Vietnam but it does explain wet-rice cultivation simply.).
In 1901 British planters introduced rubber trees into the Malay Peninsula. Commercial rubber production now takes place in Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka.
Where does rubber come from?
Hattifant Thai Animal Flextangle Papertoy Video
Recommend Books
Elephants of the Tsunami
by Jana Laiz