Ancient Egypt -- School-Age
Egypt
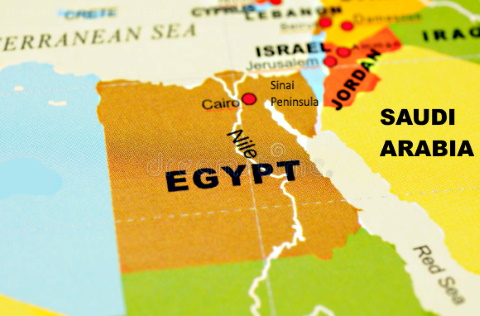
Egypt Map - Current country names used.
Egypt is Mediterranean country that is located in the northeastern corner of the African continent and the southwestern part of Asia. Egypt is a transcontinental country. A large part of Egypt is in Africa while the Sinai Peninsula is located in the Asian continent.
The Nile-The Gift of the Nile
The Nile is the world's longest river. Egypt is basically a desert, part of the great Sahara Desert. However, near the Nile River, the land is very moist and fertile. Every year, the snow in the mountains of East Africa would melt, sending a torrent of water that would overflow the banks of the Nile. When it flooded each year, the river left behind a layer of rich, dark mud on the fields. This made the soil richer and made farming easier.

The Nile River
The Nile River was the center of Egyptian life. The Egyptian people lived on the fertile lands along the Nile. A Greek traveler called this area “the gift of the Nile.”
Nile River Video
Ancient Egypt
Natural borders protected Ancient Egypt from invaders. The land beyond the Nile River Valley is a desert, to attack Egypt the invaders would have to go through all the deserts to reach Egypt. The Mediterranean Sea was a good protection against attacks on Egypt. Not many people ventured into the sea before 1500B.C.E., so the Mediterranean Sea formed a natural border. Egypt was not invaded by the sea until Napoleon in the nineteenth century.
There were 3 classes in Egyptian society: upper, middle, and lower. It also had slaves. Usually only the upper-class boys could go to school. Some middle-class and lower-class boys learned carpentry or pottery making, but most became farmers like their fathers. The girls learned skills from their mothers. The Egyptians worshipped many gods, and the king, called the pharaoh, was considered a living god on earth.
The Old Kingdom
The Old Kingdom(about 2700-2200 B.C.E)
The rival kingdoms of Upper and Lower Egypt were united by a king
named Menes,
who established his capital at Memphis.
During the Old Kingdom Egyptian culture and commerce flourished, and the great pyramids were built.
After a period of decay, Egypt entered the First Intermediate Period, a time of strife, instability and famine.

Sphinx and Pyramids in Egypt.
Middle Kingdom
Middle Kingdom(about 2050 to 1800 BCE.)
Mentuhotep II is considered the founder of the Middle Kingdom. Mentuhotep II ruled Upper Egypt from the city of Thebes.
He defeated the last of the rulers who ruled Lower Egypt, and re-unified all of Egypt. With the establishment of the Middle Kingdom, with its capital at
Thebes, Egypt grew wealthier and had more trade with other countries.
Then weak rulers allowed the country to pass under the rule of foreign nomads, known as the Hyksos.

Ruins at Medinet Abou, Thebes, Egypt
New Kingdom
The New Kingdom(about 1600 to 1100 BCE)
The New Kingdom was established and Ancient Egypt became a strong
power and built its empire.
Pyramid building was pretty much abandoned in favor of secret tombs that were not as obvious to tomb robbers.
Instead, the pharaohs directed their building projects towards temples and monuments to themselves, such as Abu Simbel built by Ramsess II and the Temple of Karnak, which was continuously built up for centuries.
These monuments and discoveries such as the finding of Tutankhamun's tomb in 1922 makes this one of the most well known periods of Pharaonic Egyptian history.

Decorated pillars of the temple at
Karnac, Thebes, Egypt.
Egypt came increasingly under foreign domination, with periods of rule by Libya, Sudan, Assyria, Nubia, and Persia.
With the conquerors came camels. The one-humped camel or dromedary was not generally used for transportation by the ancient Egyptians. The Persians used the two-humped camel as transport in the desert.